
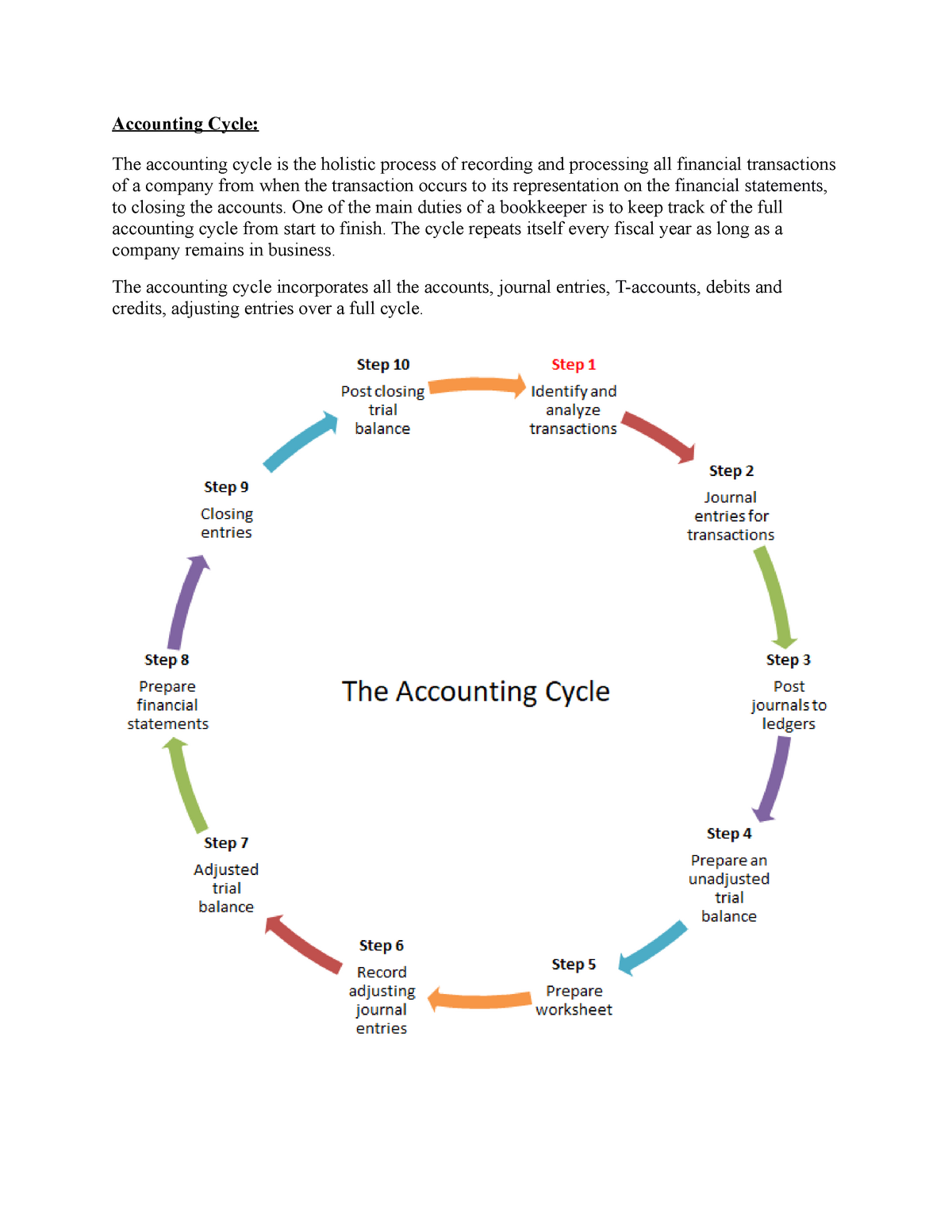
The accounting cycle is a set of steps that are repeated in the same order every period. The culmination of these steps is the preparation of financial statements. Some companies prepare financial statements on a quarterly basis whereas other companies prepare them annually.
Free Course: Understanding Financial Statements
The trial balance gives you an idea of each account’s unadjusted balance. Such balances are then carried forward to the next step for testing and analysis. In the accounting cycle, the last step is to prepare a post-closing trial balance. It is prepared to test the equality of debits and credits after closing entries are made. Since temporary accounts are already closed at this point, the post-closing trial balance contains real accounts only.
Financial Close Solution Advantages
At the end of the accounting period, a trial balance is calculated as the fourth step in the accounting cycle. A trial balance shows the company its unadjusted balances in each account. The unadjusted trial balance is then carried forward to the fifth step for testing and analysis. The accounting cycle incorporates all the accounts, journal entries, T accounts, debits, and credits, adjusting entries over a full cycle. After adjustments, there is a need to prepare a trial balance again that ensures that all credits and debits are equal. Adjusting entries are made at the end of an accounting period to adjust those accounts that need to be updated or adjusted.
- An example of identifying transactions would start with point-of-sale software.
- When identifying a transaction, you’ll need to determine its impact.
- A journal is a book – paper or electronic – wherein transactions are recorded.
- This step involves determining the titles and nature of accounts that the transaction will affect.
Try accounting software to lighten the load
Creating an accounting process may require a significant time investment. Setting up an effective process and understanding the accounting cycle can help you produce financial information that you can analyze quickly, helping your business run more smoothly. Identifying and solving problems early in the accounting cycle leads to greater efficiency. It is important to set proper procedures for each of the eight steps in the process to create checks and balances to catch unwanted errors. If you have debits and credits that don’t balance, you have to review the entries and adjust accordingly. The first step in the accounting cycle is to identify your business’s transactions, such as vendor payments, sales, and purchases.
For example, if a business sells $25,000 worth of product over the year, the sales revenue ledger will have a $25,000 credit in it. This credit needs to be offset with a $25,000 debit to make the balance zero. Whether your accounting period is monthly, quarterly, or annually, timing is crucial to implementing the how to import a chart of accounts into xero properly.
What Is the Difference Between the Accounting Process and the Accounting Cycle?
The general ledger is like the master key of your bookkeeping setup. If you’re looking for any financial record for your business, the fastest way is to check the ledger. Without them, you wouldn’t be able to do things like plan expenses, secure loans, or sell your business. Tax adjustments help you account for things like depreciation and other tax deductions. For example, you may have paid big money for a new piece of equipment, but you’d be able to write off part of the cost this year. Tax adjustments happen once a year, and your CPA will likely lead you through it.
Companies might employ multiple accounting periods, but it’s crucial to note that each period solely reports transactions within that time frame. If the accounting period extends to a year, it is also termed a fiscal year. Publicly traded firms, mandated by the SEC, submit quarterly financial statements, while annual tax filings with the IRS necessitate yearly accounting periods. The accounting cycle serves as the backbone of financial management, providing a systematic approach to track, analyze, and communicate a company’s financial health and performance. There are many essential parts of your business’s operations and keeping accurate financial records is fundamental among them.
It documents every transaction, making sure that things are accurate and kept track of. Without accounting, most businesses would be in poor financial health. Some errors could exist even if debits are equal to credits, such as double posting or failure to record a transaction. When transitioning over to the next accounting period, it’s time to close the books. Each step in the accounting cycle is equally important, but if the first step is done incorrectly, it throws off all subsequent steps. If you don’t track your transactions accurately, you won’t be able to create a clear accounting picture.
Disorganized books can lead to bad decisions, failure to fulfill various obligations and sometimes even legal problems. That’s why today we will discuss the eight accounting cycle steps you can follow to ensure accuracy. After analyzing transactions, now is the time to record these transactions in the general journal.
Additionally, many companies have to report on their financial statements due to regulations. HighRadius Autonomous Accounting Application consists of End-to-end Financial Close Automation, AI-powered Anomaly Detection and Account Reconciliation, and Connected Workspaces. Delivered as SaaS, our solutions seamlessly integrate bi-directionally with multiple systems including ERPs, HR, CRM, Payroll, and banks.
Alternatively, the budget cycle relates to future operating performance and planning for future transactions. The accounting cycle assists in producing information for external users, while the budget cycle is mainly used for internal management purposes. Bookkeeping focuses on recording and organizing financial data, including tasks, such as invoicing, billing, payroll and reconciling transactions.